Previous Page Turn page
Diabetes is the name given to a chemical imbalance in the body. that can affect a number of different organs. About one person in every 50 is diabetic, although only about one out of every four people with diabetes actually needs insulin injections for treatment.
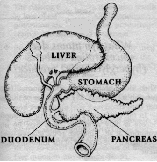
Newly diagnosed cases iniatialy have symptoms such as increased urination and thirst. These symptoms are due to the high glucose content in the urine. This in turn results from an excessive build-up of glucose in the blood. Diabetes occurs because of a partial or complete lack of insulin. This hormone is normally released directly into the blood circulation from small pockets of cells ("Islets of Langerhans") dispersed throughout the pancreas gland. The pancreas reside in the upper abdomen, just below the liver, partly behind the stomach in the loop of the duodenum. The pancreas also produces enzymes, which help with the digestion of food in the duodenum. Insulin in usable form was first extracted from animal pancreas in 1921. It has proved successful in the treatment of human diabetes.

Previous Page Turn page